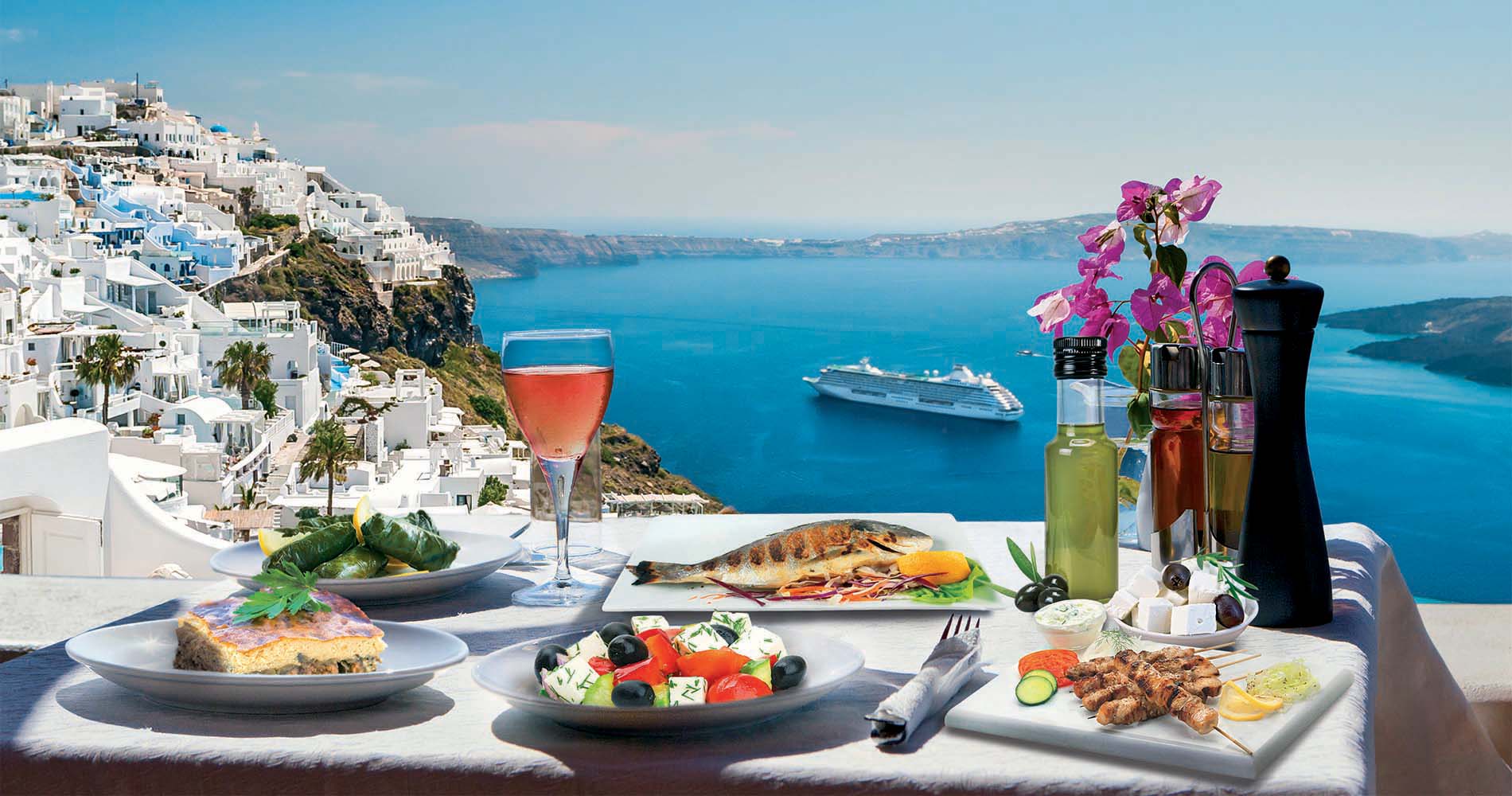
Lingering over meals with friends and family – perhaps with a glass of red wine in hand – is encouraged. The Mediterranean and paleo diets offer similar cost profiles, as both include plenty of fresh produce and some meat. In both cases, if you choose to use only organic produce, you can expect to spend more money than if you also include conventionally grown produce. The Mediterranean diet allows for plant-based foods and some animal products, like eggs, certain dairy products, and certain fish products. Followers can also enjoy starch-based veggies like potatoes. People comparing the Mediterranean diet vs. paleo foods may start their research with the Mediterranean diet, because it’s more of a modern way of eating.
No-Cook Meals for Hot Summer Days
As cited in the Harvard Medical School blog, studies have convincingly shown that the Mediterranean diet has measurable health benefits. The Mediterranean diet also encourages the occasional glass of red wine which can be a great way to reward yourself after a week of discipline. The mediterranean diet on the other hand only allows a moderate amount of meat. Nutrition researcher David Katz wrote an article in 2014 that examined the evidence behind many diets, including Mediterranean and Paleo, to determine once and for all which diet is best for health.
However, the evidence for the Mediterranean diet is much stronger. Both diets emphasize unprocessed and minimally-processed foods, which is an excellent guideline to follow. A review of 45 studies found that following the Mediterranean diet principles is linked to significantly reduced rates of total cardiovascular (heart) disease (10). The evidence for reducing blood sugar is strong for the Mediterranean diet but mixed for the paleo diet, so we need more research. Plus, it’s tough to characterize effects of the paleo diet since there are so many definitions and variations.
Blue Zones and Mediterranean Diets: What the Longest Living Populations Are Doing Right
Below, we discuss each diet in-depth, similarities, differences, and whether they’re healthy to help you choose between these top eating patterns. You have specific health goals that align with the diet’s principles, such as reducing processed foods. The same experts ranked the Paleo diet 29th with a healthy score of 2.6 out of 5.
However, I think that with careful planning – for example, consuming a wide variety of fruits, nuts and seeds – the potential for nutritional deficiencies is much lower. However, large amounts of research over the years support the Mediterranean diet’s health benefits. In addition to heart health, science has shown this diet supports a reduced risk of cancer, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. The Paleo diet’s restrictive regimen is the central cause for it being generally discouraged by nutritionists. However, you could consider using it as a starting point or baseline to introduce more whole foods into your eating pattern. Some modern variations of the diet have expanded to include gluten-free grains like rice.
Live The Paleo Diet Lifestyle
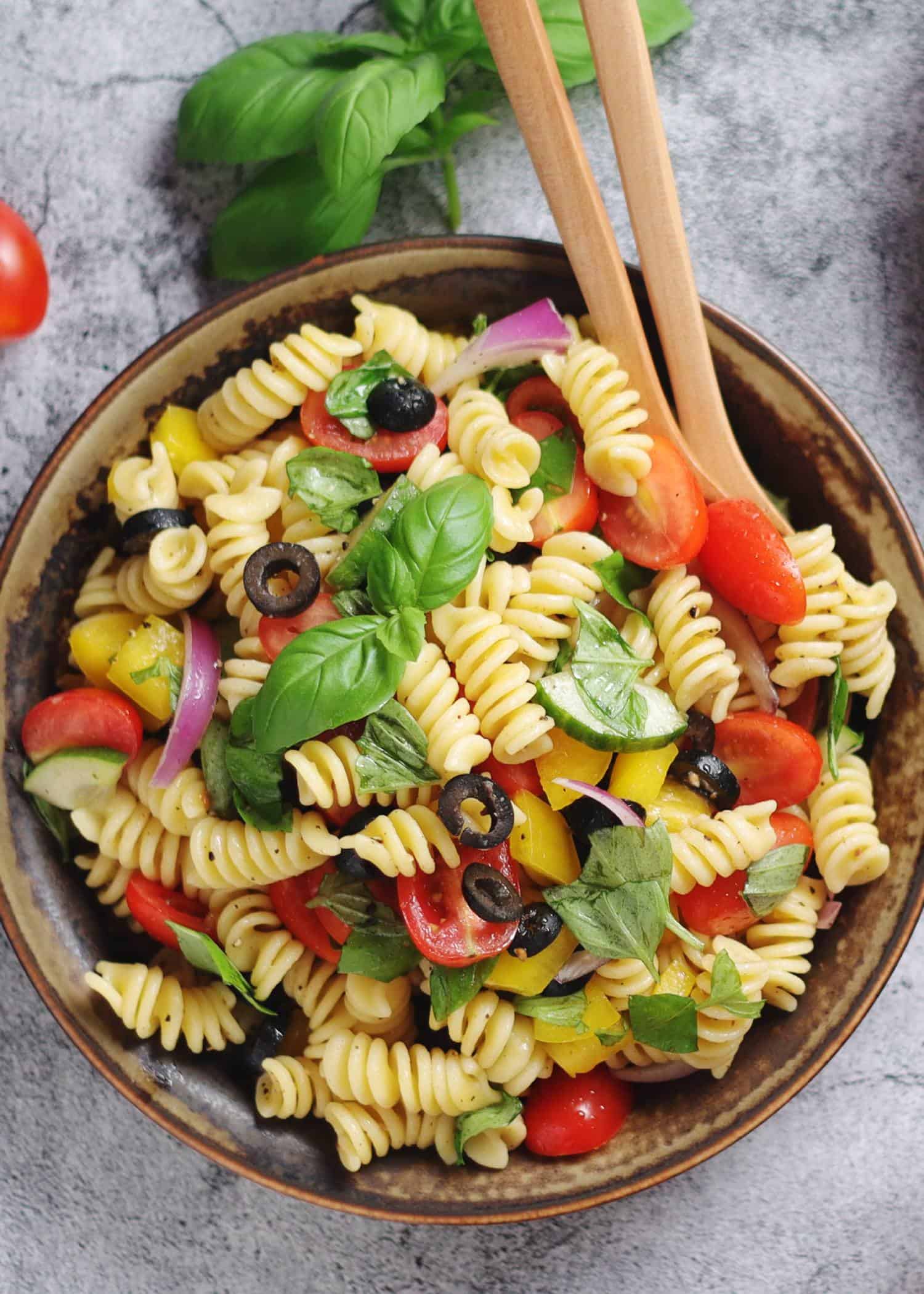
The carb content in a Mediterranean meal is confined to unrefined fibrous sources such as vegetables, fruits, beans, and whole grains. The paradigm shift in the eating patterns of humans has resulted in modern methods of food preparation. The agricultural revolution entailed the evolution of man from a hunter and gatherer to that of eating more processed grains.
Planner A: Busy professional aiming for heart health and steady weight loss (Mediterranean)
Therefore, the Mediterranean diet is more beneficial than the paleo diet to overall health because it does not eliminate these essential food groups. Any diet can have health risks, especially if you do not consult your doctor before changing what you’re eating. Overall, both diets are considered healthy, though there are some notes to keep in mind. It’s okay to experiment, make adjustments, and find a way of eating that makes you feel your best.
Mediterranean Diet vs Paleo: How Do They Compare?

It’s easy to overeat high-calorie stuff like olive oil and nuts without strict rules. Inflammatory cytokines are proteins that are believed to play a role in causing heart disease and heart attacks (21). In comparison to the paleo diet, a review of 56 studies concluded that the Mediterranean diet was more effective at reducing fasting blood glucose and A1c in those with type 2 diabetes (7).
Scientific studies supporting the Mediterranean Diet
Often, people will eat a paleo diet for a short time, then fall back on their previous way of eating. On the other side, the Mediterranean diet is known for its heart-health benefits. According to a 2018 study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, adhering to the Mediterranean diet can reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and death from heart disease by about 30%.
FAQs: Understanding the Mediterranean and Paleo Diets

Both diets have been popular for years, and as a result, extensive research has been conducted to examine their effects on health. Your choice should align with your cultural preferences, health goals, and lifestyle needs. Since inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein can also increase due to infection, a single indicator of inflammation may not be an accurate measure of chronic inflammation. A cross-sectional study among 646 adults suggests that both the Mediterranean and paleo diets are linked to lower levels of inflammation and oxidative stress (18). Since the definition of “processed” may be confusing, an international panel of food scientists and researchers developed NOVA, a classification system for food processing.
A Healthy Keto Recipe That’s Full of Protein and Healthy Fats
For example, as we discussed, the Mediterranean diet has been extensively studied and linked to numerous health benefits, particularly the prevention of cardiovascular disease. On the other hand, if your primary goals are weight loss and improved body composition and blood sugar control, the Paleo diet may better offer these potential https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/22466-low-fodmap-diet health benefits. Either way, always consult your healthcare professional before starting any new diet.
Heart-Healthy Mediterranean Plant-Based Cooking: A Recipe for Longevity
You enjoy a variety of foods, including whole grains and dairy. While it may be effective for short-term goals like weight loss, its exclusion of entire food groups may make it less sustainable in the long run. Additionally, the diet’s heavy reliance on animal products raises concerns about environmental impact and ethical considerations. Your choice should match your health goals, preferences, conditions. Always best to talk to a healthcare provider or nutritionist for tailored advice. Beyond weight loss, it’s great for overall health, especially heart health.
Proponents believe that this has “discordance” has led to today’s problems of obesity and heart disease. This diet is characterized by trying to mimic how we think our hunter-gatherer ancestors in the Stone Age (2.5 million to 10,000 years ago) ate. Farming wasn’t introduced until around 10,000 years ago, so cultivated foods such as wheat and potatoes are a no-no on this diet.
- The restriction on carbohydrates drives the body to use fat for energy expenditure and prevents the rise in insulin levels, which helps curb hunger.
- Both ways of eating have pros and cons, so it’s essential to consider your health goals before making a choice.
- Therefore, it is essential to avoid processed and refined foods as much as possible.
- As you can see, there are a number of similarities between the two diet plans.
- According to the Mayo Clinic, studies suggested that the Mediterranean diet does reduce a person’s risk for cardiovascular diseases.
- Like any diet, there are potential downsides to a Mediterranean lifestyle.
Potential Weight Loss:
When determining which diet is right for you, consider your health goals, needs, preferences, and access to foods. Paleo diets may be too restrictive for some people, so if you want to follow it, ensure you eat lots of variety. According to the diet, human metabolism has been unable to adapt fast enough to handle many of the foods that have become available since the start of agriculture. Hence, the human diet remains best adapted to the diet of their Paleolithic ancestors. These new foods have led dumascoop to modern-day problems such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
